Technical Notes: Applications
Your knowledgebase for DAISOGEL silica gel products
-
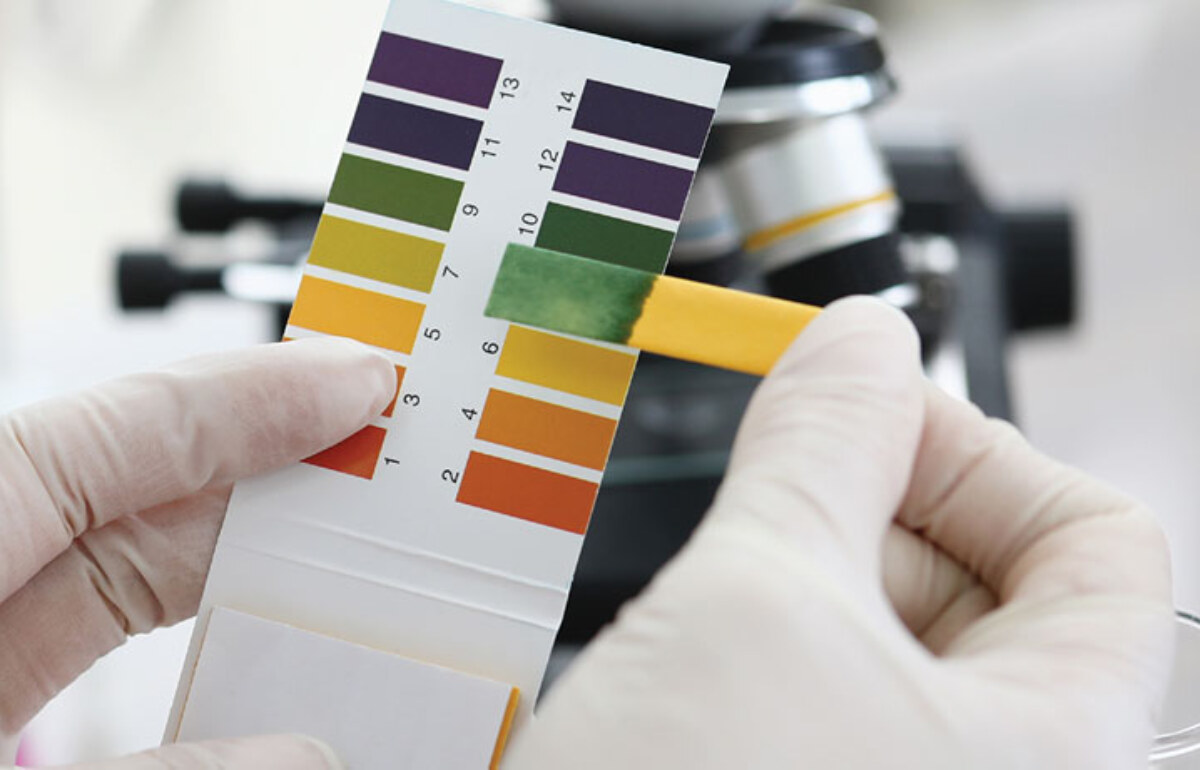

What is the pH Range of DAISOGEL C8 and ODS Phases?
Read More >Are you purifying a compound that requires a very low pH condition for solubility or elution purposes? Perhaps you need a silica gel that can withstand caustic cleaning instead. The pH stability of a C8 or ODS silica gel is dependent on the robustness of the bare silica gel, as well as the ligand density and the quality of the bonding. DAISOGEL offers a wide range of bonded phases with various ligand densities to give you choices for finding the right match for your application. Your guide to the pH range of our most common C8 and ODS phases: Contact
-
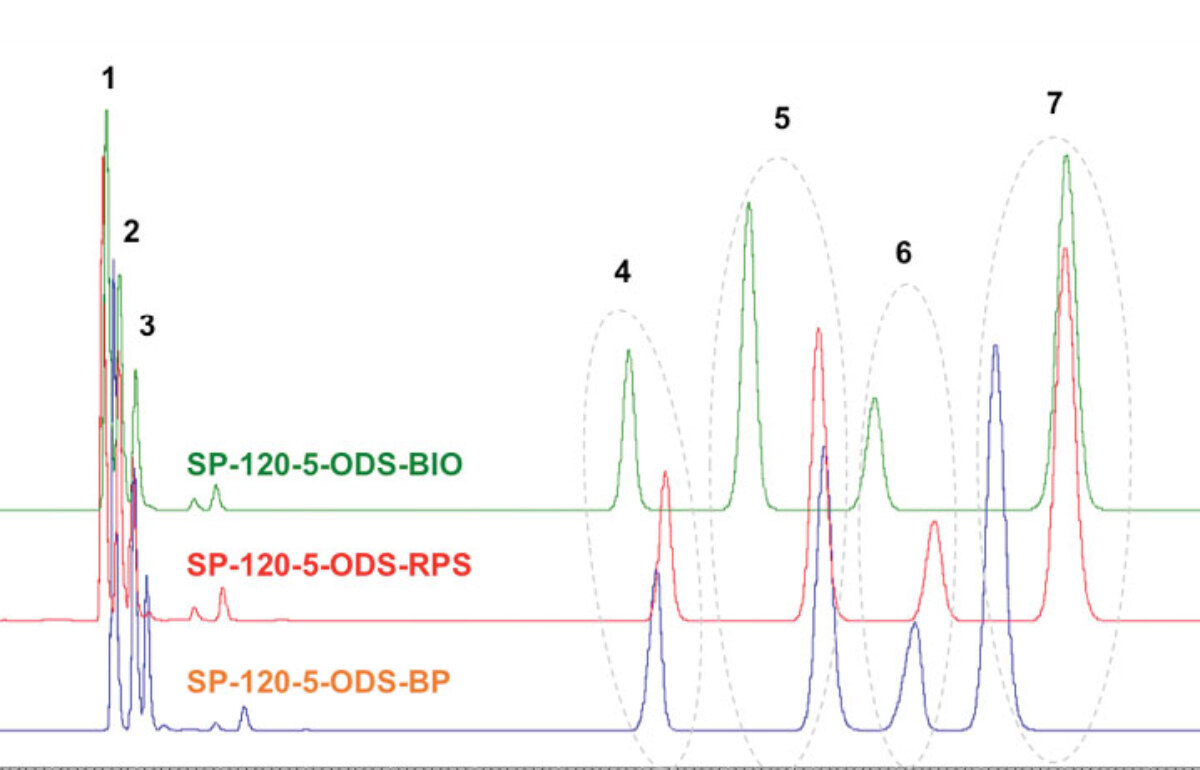
What is the Role of Ligand Density for Separation?
Read More >When meeting with potential bulk silica customers for the first time, we are often asked the following question: “Do you have an ODS/C18 phase?” While the answer is, of course, a resounding yes, we also suggest that this is not the right question to be asking your silica gel supplier! The right question is: “What different ligand densities do you offer for your ODS/C18 phases?” With ligand density (sometimes called bonding density), we express how much of the given ligand is grafted onto the silica’s surface – not only onto the outer particle surface, but also on the INSIDE of
-

Which DAISOGEL grade is best for small molecule purification?
Read More >The key for a good small molecule separation–or any chromatographic separation, for that matter–is that your target molecule has access to the entire surface area of the silica gel-based stationary phase. The pore size of the bead must be wide enough for this purpose, yet small enough for the silica product to have a large enough surface area to provide an effective loadability and ensure optimized process economics. In fact, the surface area and the pore size have direct correlation in DAISOGEL products. For small molecules, there is one grade in particular that strikes the right balance between pore size
-
Particle Size Discrepancy Between Bulk Silica Gel Products
Read More >When you work in a purification process development laboratory, you undoubtedly want to screen several silica gel products from various manufacturers in order to determine which silica product has the best selectivity and overall yield for your given API. To design a robust screening study, the process development scientist knows to compare “apples to apples.” It might not be well-known, but there can be a difference in the particle size values published on Certificates of Analysis (so-called “nominal” size) versus actual particle size with some silica gel suppliers. Naturally, different particle size measurement methods will yield different results, and to
-
Which DAISOGEL grade is best for recombinant peptide purification?
Read More >Recombinant peptides are therapeutics produced from the recombinant DNA method, a technique which allows for much longer and more complex peptides to be produced. Production starts with fermentation using a microbial host, such as the bacterial microorganism E. coli, or a yeast-based microorganism such as S. cerevisiae or, more recently, the methylotrophic Pichia pastoris. These microorganisms are engineered to express the recombinant peptide of interest during the fermentation process. Unlike the synthetic method of peptide production, the recombinant method produces a significant amount of host cell debris, glycosylated proteins, and other impurities that must be removed after harvest. In addition,
-
Which DAISOGEL grade is best for synthetic peptide purification?
Read More >While there isn’t one general answer, let’s start with some background on the different types of peptides and their makeup. In general, there are two upstream modes for large-scale production of peptide-based APIs: Synthetic method: solid-phase peptide synthesis (SPPS) using amino acid starting materials and either Boc or the milder Fmoc chemistry; Recombinant DNA method: recombinant production from microorganism culture such as E. coli Peptides produced using the synthetic method are generally very clean and do not require as much purification compared to the recombinant peptides. The recombinant DNA method enables the production of much longer and more complex peptides;
